Davies-Sumatra
Tracing Thomas Richardson Davies Ancestors
Y-DNA Paternal Ancestry upd
Phylogeography of R-U106 by Iain McDonald. December 2, 2025.
This white paper describes methodologies and data relating to the phylogeographic spread of the Y-DNA haplogroup R-U106 and its sub-clades. This is not meant to be an authoritative and fully correct account of the growth and spread of R-U106, it merely aspires to be less wrong than existing alternatives. While complete, this remains a work in progress, with many loose ends: don’t expect perfection!.
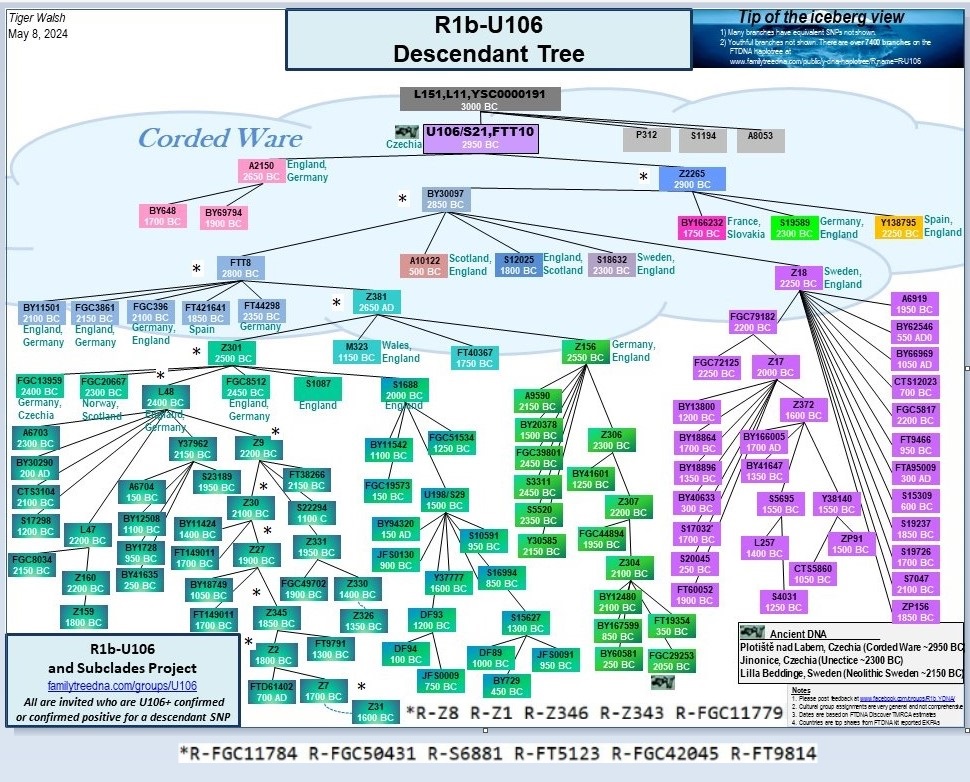
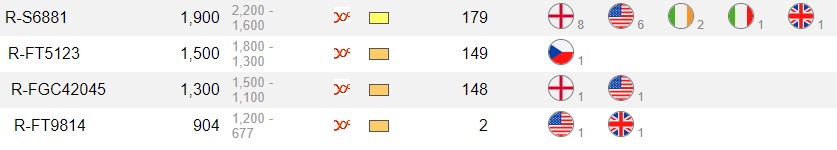
p. 167 Overall, this then gives us little indication of distribution, outside of a couple of sporadic points in southern England. R-FGC42045 dates to between the sixth and tenth centuries, and likely represents an Anglo–Saxon-era family living in England. It has six sub-clades:
R-FT9814 is my haplogroup (FTDNA BIG Y-700)

SNP markers A single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) is a change to a single nucleotide in a DNA sequence. The relative mutation rate for an SNP is extremely low. This makes them ideal for marking the history of the human genetic tree. SNPs are named with a letter code and a number. The letter indicates the lab or research team that discovered the SNP. The number indicates the order in which it was discovered. For example M173 is the 173rd SNP documented by the Human Population Genetics Laboratory at Stanford University, which uses the letter M.
Sapp Tool
Sapp tool by David Vance (free). To analyse and to make all DNA data more visual and "understandable". I use it only to upload a list (txt file) with the 111 STR markers (download YDNA in csv format) and kitnummers (or names) of a FTDNA surname projectmember (s) for a analysis of the DNA relationship. Results: Table of SRT data, GD Genetic Distance*, Kit (or Name) to SNP & Genealogy Cross-Reference. *Genetic Distance is the number of differences, or mutations, between two sets of results. A genetic distance of zero means there are no differences in the results being compared against one another, i.e., an exact.
STR markers are used for more recent genealogical testing and comparison, while haplogroups (FGC42045) reach further back in time.
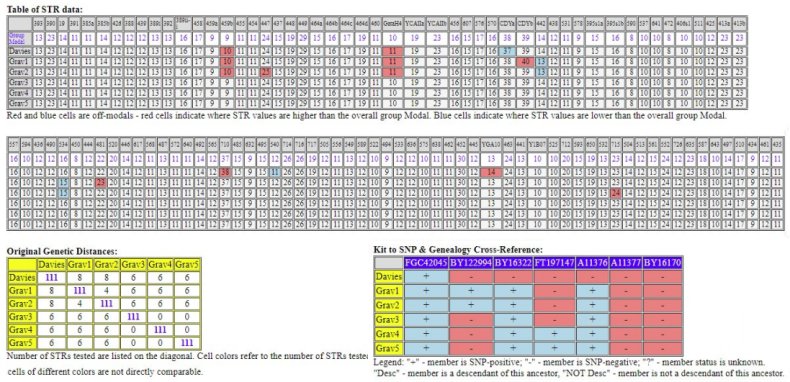
Compare my (above) 111 STR markers with those of testers of the same surname (Gra1-5) and (below) my first 40 STR markers with those of surnameproject members with different surnames.
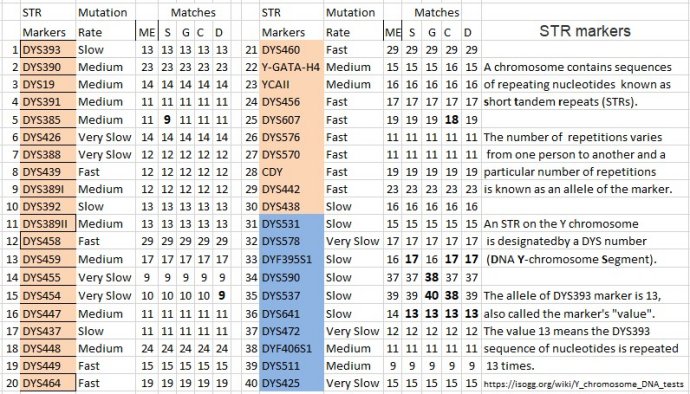
Did England once have a few powerful patrolynic clans? By Admin/Author Robin Spencer (FTDNA Project group: England GB Groups EIJ)
There are hints in the Y DNA. For another purpose I recently compiled a table of 1600 Anglo-Irish clades, each defined by a specific SNP formed around the time that surnames arose and each with a list of all the surnames of its descendants -- not including haplogroups formed after 1630 since I want to avoid additional surnames due to colonial NPEs. Sorting in order of distinct surnames per clade gives the table above. Some well-known Scottish and Irish clades immediately jump out. R-S744 caps an Alpin-Stewart line whose descendants have 49 different surnames today. R-FGC5623, a bit down from R-L226, is the Dalcassian line of Brian Boru, the O'Briens. Somerled's Vikings-to-MacDonalds are under R-YP330, and so forth, including several well-known clan names. The hypothesis holds up: a patrolynic clan that held early medieval power and influence may be recognized today by a large number of descendant branches with a variety of surnames, some of which will match history or legend. A chieftain with many surviving grandsons before surnames appear means many diversely named descendants today. So the curiosity: among the top 21 such clades there are three very English ones, each with many surnames but none with a historic ring. Are these the descendants of forgotten patrolynic clans? In Ireland and Scotland such clans persisted for centuries after 1066 and were written down, but in England, the conquering Normans might have destroyed the evidence in two ways: first, simply by subjugating them militarily, and secondly, by imposing surnames from their own traditions (occupational, descriptive, locational) rather than clan-patronyms.
So the largest of these English clades is under R-FGC42045 (mostly R-A11376), surnames Warburton, Bland, Graves, Haworth, and located in Lancashire. Never heard of them?
Yet the DNA suggests it was huge, comparable to the kingdoms of Brian Boru or Somerled. Same for the clan under I-FT3552, surnames Powell, Thomas, Hadley, Jones -- strongly Welsh. How did a Viking line beget a Welsh chieftain in only a few generations? That's a good project for a historian.
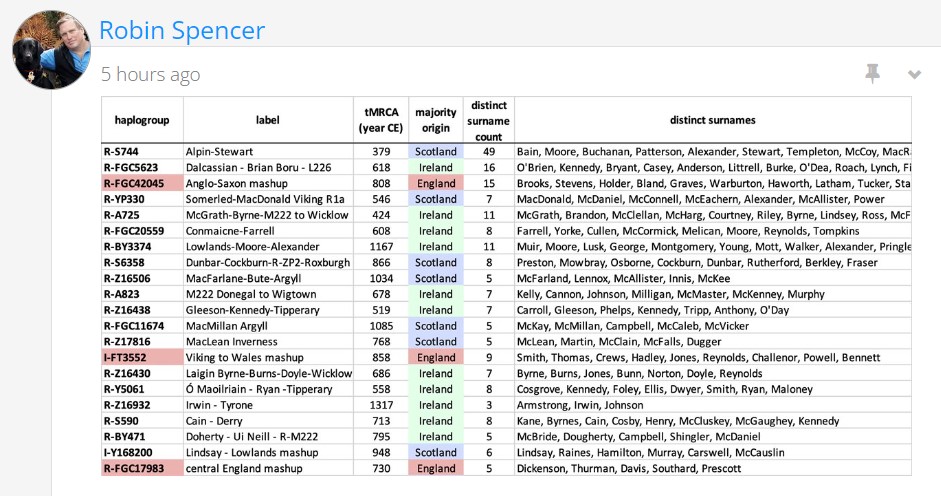
By Arthur Baker (FTDNA Project group: England GB Groups EIJ)
Although I've mentioned the rarity of the Welsh Tribe allele value of 13 for DYS570 before, as they say, one picture, in this case from YFull, is worth a thousand words. This not only shows their rarity among R-P312 men in "R1b", but also what their modal (most common) value is, which is 17. It also provides information to testers with other allele values about how rare their allele might be and the range of allele values that it spans. That range also contains important information about how wide it is and whether it exhibits progressive or regressive tendencies.
Rb1-M343 Descendant Tree (Facebook R1b Y DNA project)
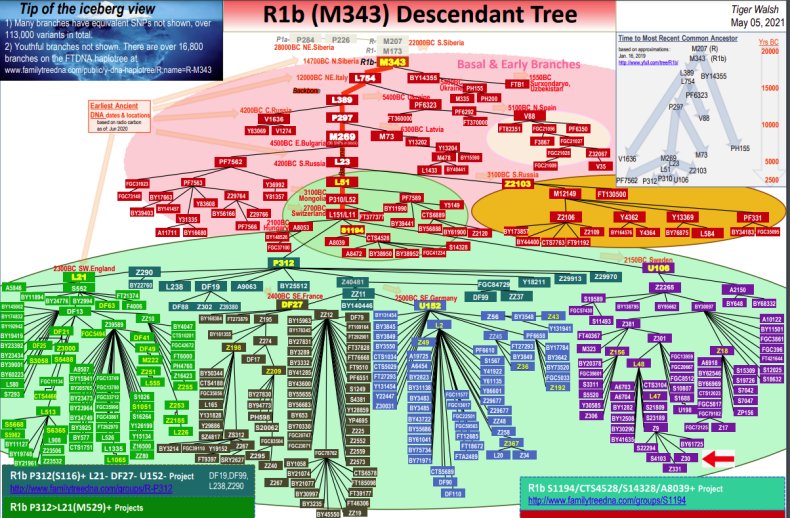
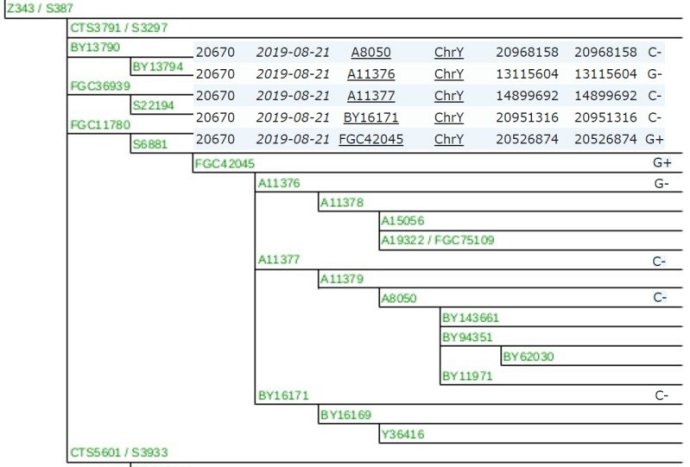
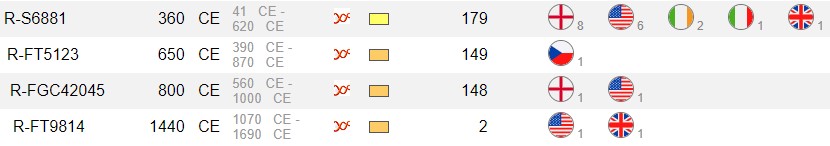
Y-DNA Haplogroup FCG42045, this branch is definded by the Y-Haplotree at FamilyTreeDNA. Parent Branch is R-S6881 - R-FT5123 and Descendant branches R-A11376, R-A11377 and R-BY16170. Big Y Block Tree is a block diagram of the Haplotree showing the relationships between me and other Big Y testers. Branch lengths can represent evolutionary time, calculated as number of mutations.
Very, very distant Y-DNA 111 "matches" family members Richardson & Williams (GD 5, both also tested Big Y-700)
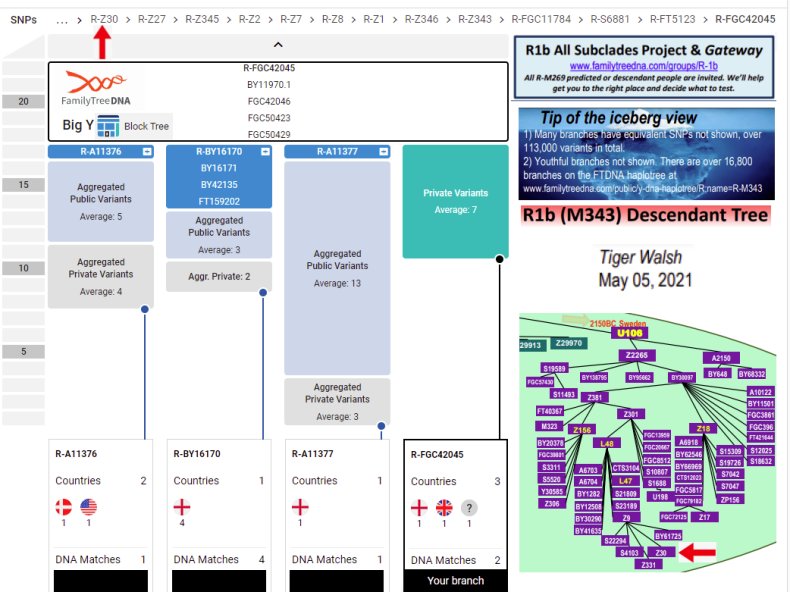
FTDNA Block Tree Haplogroup FGC42045 (my branch).
R1b-U106 Descendant Tree *U106-FT9814 (Facebook R1b Y DNA project)


FDNA Group Projects: Davis/Davies/David; R _R1b ALL Subclades; R U106 R1b-U106; M* & all M mtDNA; Davenport; Graves; Richardson; Smith; Stanley; Warburton; Lancashire, British Isles by County; Germany-YDNA; Families In British India; Welsh Patronymics; Scottish Mapping.
YSEQ DNA Origins Project. Test Haplogroup L48 panel (paid). "L48 is the largest sub-group below R1b-U106. With this DNA test we start with 5 key SNPs: L47, Z9, Z2, Z8, Z326 and then we work down the branches iteratively until we have found your position on the given tree. The test is completed when the unique phylogenetic position on the tree has been determined". Result: I am negative for haplogroups A11376, BY16170 and A11377. (see also Block Tree)
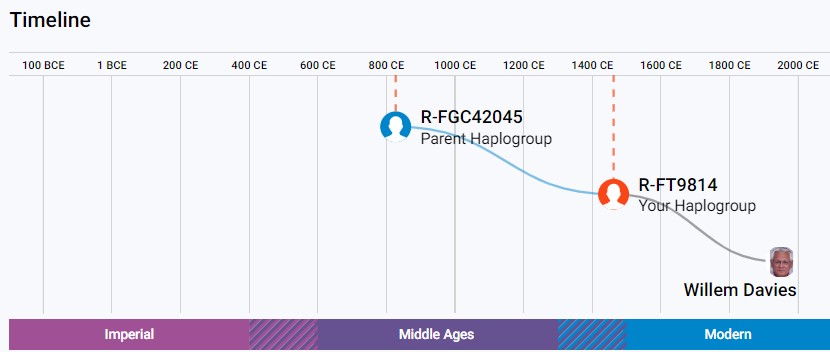
allows you to enter a SNP name (FGC42045) and to see: (1) a migration map; (2) migratory timelines; and (3) a SNP path showing chronology for each upstream SNP. The maps are intended to show where SNP mutations occurred. Most map locations are based on an average of the self-reported locations of tested men. FGC42045 end up for the time being in England aprox. 800 CE.(CE stands for “common (or current) era”, while BCE stands for “before the common (or current) era”).
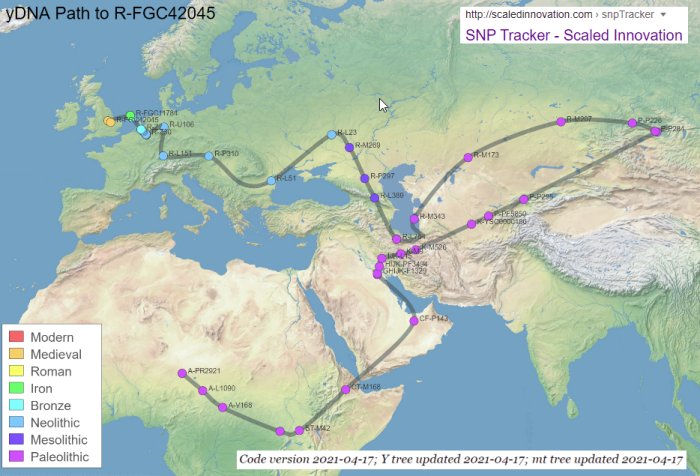
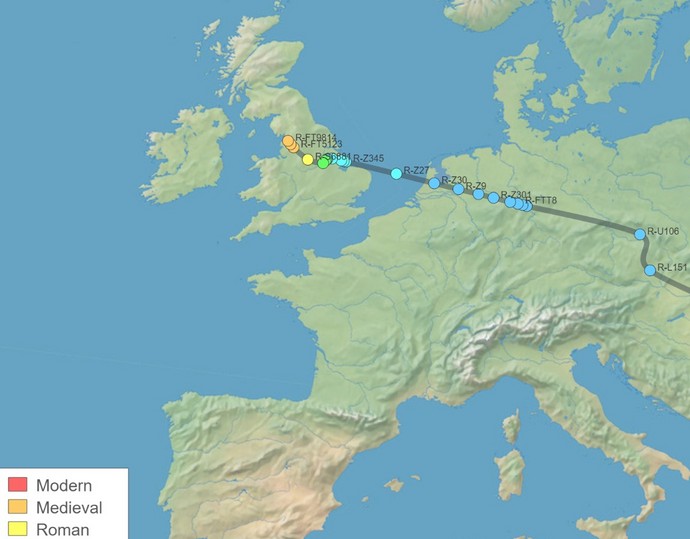
SNP Tracker. This tool creates a map which traces a paternal line from human origins to any Y or mitochondrial SNP
Code version 2022-09-20; Y tree updated 2022-09-18; mt tree updated 2022-09-18
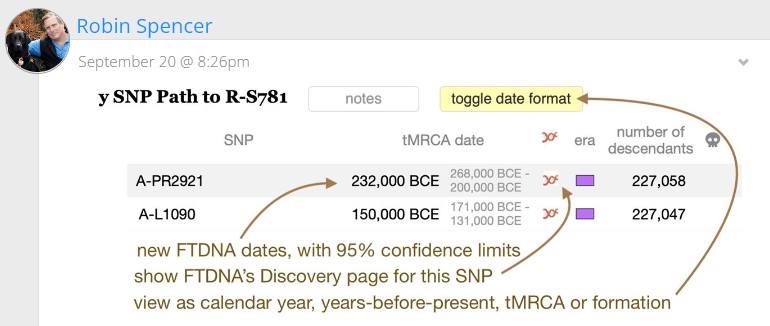
tMRCA or formation dates,
in units either of calendar years (BCE/CE) or as years-before-present. Have a look at http://scaledinnovation.com/gg/snpTracker.html?snp=s781 .

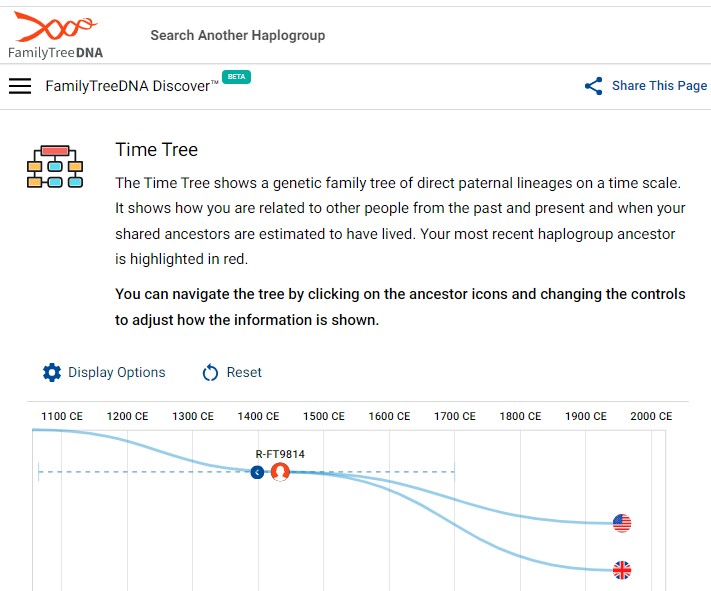
FTDNA Your Y-DNA Haplogroup Report for R-FT9814 Story (upd. 9-2022)

The Y chromosome is passed on from father to son, remaining mostly unaltered from generation to generation, except for small trackable changes from time to time. By comparing these small differences in high-coverage test results, we can reconstruct a large Family Tree of Mankind where all Y chromosomes go back to a single common ancestor who lived hundreds of thousands of years ago. This tree allows us to explore paternal lineages through time and place and to uncover the modern history of your direct paternal surname line and the ancient history of your ancestors.
FTDNA Your Y-DNA Haplogroup Report for R-FT9814 (Sep 2022) Notable (FUN pages) & Ancient Connections.
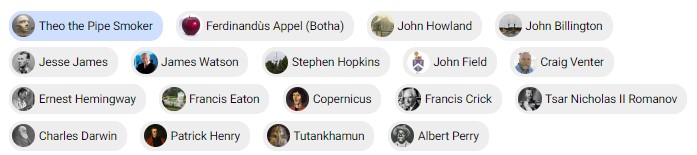
Facebook FTDNA User Group sept 2022. Discover had another update today with some new branches and ancient samples added, but the bigger news is a new feature called the Time Tree.

use Browser Back or My Autosom, Y-DNA & MtDNA (Main Page)
Back to Top of page